There are many types of arthrosis.For example, hip joint disease is called coxarthrosis, and knee disease is called gonarthrosis.
The treatment method for all subtypes is usually the same.But still, many people do not know the difference between arthrosis and gonarthrosis of the knee joint.
On this basis, many erroneous uses of these terms have appeared among patients with this problem.
Causes
Gonarthrosis is a disease of the knee joint with damage to cartilage tissue.Many people mistakenly believe that the disease is typical only for the elderly, as it is degenerative.But, as practice shows, gonarthrosis appears more often in young people.
This is confirmed by the causes of the disease:
- knee injuries (breaks, dislocations, cracks);
- weight lifting, vigorous physical activity without proper training;
- inflammation of the joints due to exposure to various factors, including hypothermia;
- excess weight, as it leads to a large load on the joints and their subsequent degeneration;
- genetic predisposition.
As you can see, all factors for the occurrence of gonarthrosis are more typical for young people, as they lead an active lifestyle.
Although, due to excess weight, the disease can also appear in pensioners.According to statistics, after 50 years, gonarthrosis appears more often in women.This is due to the restructuring of the body, changes in metabolic processes.
Principles and types of treatment
Arthritis is generally a chronic disease, so it takes a long time to treat them.Therapy can be surgical or conservative.
With the first and second methods, doctors try to somehow influence the cause of the disease, as well as eliminate the pathological symptoms.
It should be noted that surgical intervention is more typical for stages 3-4 of arthrosis.In the fourth, it is inevitable, and in the third, you can still try to overcome the disease using conservative methods.
In addition, it is recommended to use special groups of gymnastic exercises, for example, the Bubnovsky technique.
In addition to the destruction of cartilage by gonarthrosis, muscle fibers and ligaments are susceptible to destruction.The purpose of the treatment is:
- pain relief;
- elimination of inflammation;
- removal of edema of the periarticular area;
- stopping the destruction of cartilage, its full or partial restoration;
- return to a full life and freedom of movement.
Even in cases where a person cannot completely cure arthrosis of the knee joint, he can partially return to a normal lifestyle thanks to therapy and prevention.The condition persists until the next rollback.
Conservative method
This method of therapy is used in most cases and is the main one.As a rule, patients are treated in this way in the initial and middle stages of gonarthrosis.All actions involve the use of medications (tablets, capsules, injections) with chemically active substances.
The following can be prescribed for treatment:
- analgin;
- chondroprotectors;
- nonsteroidal drugs;
- synovial prosthesis;
- glucocorticosteroids.
Other conservative methods include treatment with various ointments, mud baths, etc.
Recently, gymnastics and light physical exercises have become very popular to stop the course of the disease or the possible recovery of the patient.
The body reacts very well to non-steroidal drugs.However, they are widely used in the treatment of arthrosis due to their multifunctional action:
- elimination of swelling in joints;
- pain relief;
- treatment of inflammatory processes.
Because of these properties, doctors are increasingly choosing these drugs over traditional analgesics.
Glucocorticosteroids are synthetic drugs that can replace natural hormones produced by the adrenal glands.If we compare them with non-steroidal drugs, glucocorticosteroids are much stronger.In addition, they have an anti-allergic effect.
Chondroprotectors act directly on the cartilage and are completely safe treatments for knee arthrosis (gonarthrosis).They are obtained from animal bone structure, fish cartilage and crustacean shells.Medicines are a building material for cartilage, they improve metabolic processes and proper nutrition of the joint.
In addition to the use of medications, the following are prescribed during treatment, recovery and prevention:
- physical therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- various massages;
- visiting sanatoriums and resorts.

All this enables the patient to return to normal life and adjusts the result obtained with conservative treatment.
Moreover, the classes are easy.A very useful exercise for the knee joint with gonarthrosis is to roll with your foot a ball placed on the floor or another cylindrical object, for example, a flip flop.
Surgical intervention
If it is not possible to cure the disease with the help of drugs or therapeutic exercises, then it is necessary to undergo surgery.It can be done in open and closed joints.At the same time, surgical methods are improving every day and new methods are added to the previous ones, performed with modern equipment.
New methods of performing operations include:
- microsurgical intervention to restore damaged cartilage tissue;
- laser beam treatment with the necessary characteristics - thickness, power, etc.;
- creation of an electrolytic plasma field with a thickness of 1 mm;
- arthroscopy;
- endoprosthetics - replacement of joint parts with artificial prostheses.
Modern surgical methods are low-traumatic and allow a large number of different manipulations with the joint.
Recipes of traditional medicine
Conservative methods of treatment cannot always give the maximum result in the treatment of gonarthrosis.Recipes of traditional medicine can be used as additional medicines.
To get rid of knee pain and stiffness, you can use the following recipe:
- 150 g of garlic;
- 4 lemons with peel;
- 250 g of celery root.
Grind all the ingredients in a meat grinder, mix and pour boiling water.Then put it in a pot, cover tightly with a lid and cool.Take 60-70 g 3 times a day for a month.If pain appears, you can repeat the course or perform it every six months for prevention.
You can also use this recipe:
- beat two eggs and mix with 4 spoons of salt;
- Apply the mixture to a bandage and apply to the injured area.
The procedure should be repeated twice in a row.Do not remove the bandage until the mixture dries.
To make a medicinal ointment, you will need the following ingredients:
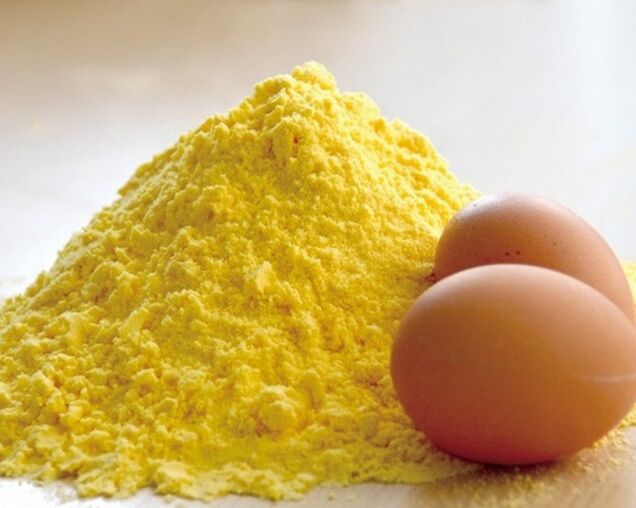

- 200 g of alcohol;
- 4 egg whites;
- 50 g of camphor;
- 50 g of mustard powder.
Add mustard and camphor alternately to the alcohol.Beat the egg whites in another bowl and then mix them together.The ointment is applied to the injured area.
Of course, heavy physical activity in athletes is a common cause of gonarthrosis as well as aging of the joints over time.
But recently, cases of the appearance of the disease without such underlying causes have become more frequent.People, on the contrary, lead a sedentary lifestyle, which is why they gain extra pounds.
The load on the joints increases and prevents them from remaining healthy for a long time.
The difference between arthrosis and gonarthrosis
Not everyone understands the difference between gonarthrosis and arthrosis of the knee joint.Gonarthrosis is characterized only by damage to the knee, while arthrosis itself is the name of a group of joint diseases that can affect any joint.
In medical theory, there are many diseases whose names contain the part "arthrosis" - osteoarthrosis, polyarthrosis, coxarthrosis, gonarthrosis.In this regard, the ignorant do not always correctly understand the meaning of each of them, thinking that they are all synonyms.
Gonarthrosis can be easily confused with the following diseases:
- arthritis;
- vascular pain in the knees;
- periarthritis - inflammation of the knee tendons;
- meniscus damage.
But it is still possible to distinguish gonarthrosis from these diseases.For example, meniscus damage (meniscopathy) is a disease that begins with sharp and sudden pain in the knees after unsuccessful movements, and gonarthrosis develops and progresses over the years.If meniscopathy is not treated, pain will occur from time to time, but bone deformity will not occur.
With coxarthrosis (disease of the hip joint), reflex pain is often felt in the knees, but the two diseases can be distinguished from each other in the following ways:
- with gonarthrosis, a person can calmly move the legs at the hip joint, spread them;
- with coxarthrosis, on the contrary, the patient can bend and straighten the knee freely;
- if the pain is felt in both joints, then we can assume that this is polyarthrosis.
Arthritis is characterized by inflammation of the joints and a sudden onset, but the pain does not affect the mobility of the joints (as with periarthritis) and is eliminated thanks to warming ointments.With this disease, swelling, high temperature and increased pain occur at night.
Vascular pain occurs due to blood circulation disorders - this often affects young people under 20 years old.This is due to the rapid growth of the whole organism.
Thus, arthrosis is the general name of the disease, and gonarthrosis is a name that indicates the location (knee).Therefore it is correct to say either "arthrosis of the knee joint" or "gonarthrosis", but not "gonarthrosis of the knee joint".And it is quite possible to determine an accurate diagnosis through careful research and personal observations.
Arthrosis of the knee joint (Gonarthrosis): diagnosis and treatment
The knee joint is a wonderful flexion-extension mechanism provided by nature.At rest, it appears only in disabled people and obese people who have lost the ability to move.
Count how many times a day you move and you will come to the conclusion that the knee is the most mobile part of the joint.No wonder diseases often choose it as their target.
One of them is gonarthrosis or arthrosis of the knee joint.
Causes of arthrosis of the knee joint
It's hard to say what causes early cartilage loss in some people.It is generally believed that the culprit is a metabolic disorder, in which the metabolism of amino acids and important trace elements occurs slowly or incorrectly.
Here, on the other hand, the following reasons should be blamed:
- Certain immune-related diseases (for example, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Self-neglect: sports and movement, nutritious food containing a full range of vitamins, amino acids and minerals are often pushed aside by people somewhere far away for "later" ("I'll start on Monday, of course")
- From birth, the natural balance is disturbed - the so-called hereditary causes.It is very easy to verify your genetic predisposition: see what your grandparents got sick with and ask what their ancestors were sick with.
- Disturbance of hormonal balance: such disorders especially affect the female body during a period of estrogen deficiency, an important hormone necessary for osteosynthesis.It is not for nothing that most of the victims of arthrosis are women of a wonderful mature age, when they are not yet old, but already wise, that is, the "over 50" mark.
- Vascular diseases: Arthrosis is often combined with venous insufficiency, venous thrombosis and other diseases.
- Mood: If you think stress only puts you in a bad mood, you're wrong—stress can slow your metabolism into a state of suspended animation.
- A risk factor for osteoarthritis is excess weight
What symptoms allow one to suspect this bad pathology?
Symptoms of gonarthrosis by stage
Each stage has its own distinctive features, but they are united by the gradual development of the disease:
You cannot suddenly stop walking because of pain: a sharp and sudden symptom of knee pain is most likely to indicate an injury.
The first stage.In the first stage, the following symptoms appear:
- Slight pain after a long walk, climbing stairs, etc.
- Stiffness after rest
- There is no deformity in the knee, but it may be somewhat swollen due to accumulated fluid: this phenomenon is called synovitis.Fluid can even collect in the back - the popliteal fossa, forming a cyst, which is often confused by frightened patients with a cancerous tumor.The cyst usually resolves easily after treatment with injections of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) or glucocorticosteroids
The second phase
In the second stage, the following signs are observed:
- Increased pain after exercise and movement and the appearance of a characteristic sharp crackling
- Increased stiffness in the morning
- Movement all the way or even 90 degrees is accompanied by a symptom of pain, sometimes so strong that it becomes impossible to complete it.
- Due to the onset of deformation, the bones thicken and become hard - this can be determined by palpation
- Synovitis may worsen
The third stage
In the third stage, which has already been defined as late deforming arthrosis of the knee joint, symptoms appear:
- Constant pain that does not go away even at night: the knee hurts and twists, especially in cold, damp weather
- A sharp decrease in the range of motion: no more than 90 degrees, or even less
- Changes in gait: the patient begins to limp, walks slowly on half-bent legs, walks, walking uphill is especially difficult.
- Visible severe deformation with the mixing of the joint axes - because of this, the legs take the shape of the letter "X" or "O" (such signs are called hallux valgus).
- At this stage, the cartilage, as a rule, is already completely destroyed, and ossification (ossification) occurs in the ligaments.
- Then, the surface of the joint becomes overgrown with calcium deposits, which is why the knee takes on a bumpy and uneven appearance.
- Due to severe deformation and lack of synovial fluid, movements in the knee become extremely painful
- Gradually, almost complete immobility of the knee is established - late deforming arthrosis of the knee joint
Treatment of gonarthrosis
The treatment of this disease is complex and long, effective only in the early stages.In the latter, conservative treatment plays a role only in mitigating the patient's situation.
Diagnosing.An important preliminary stage is diagnosis.
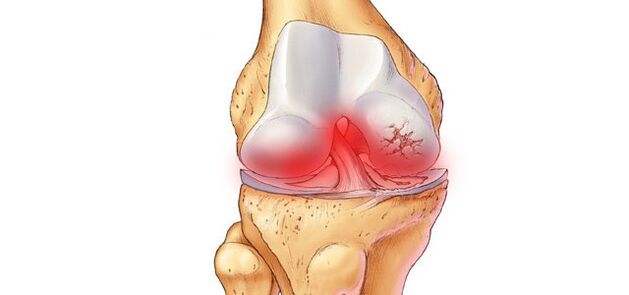
- The best way to diagnose and determine if the pain is caused by injury or osteoarthritis is by using an X-ray or MRI of the knee joint.
- Osteoarthritis is diagnosed if there is: degeneration or absence of cartilage tissue and a small gap between the joint and the capsule.
Conservative treatment
During exacerbations, the most important condition for treatment is:
- Maintaining rest and light exercise
- Taking sedatives (for severe pain - in the form of intra-articular injections)
- In the third and fourth stages of arthrosis, liquid injections are also prescribed to lubricate the joints.
For gonarthrosis, the following types of physiotherapy are effective:
- SWT (shock wave therapy)
- electromyostimulation
- acupuncture
- magnetic therapy
- radiofrequency therapy, etc.
Rehabilitation treatment
To avoid contractures and even greater immobility, knee exercises should be started immediately after acute pain subsides - for this, exercise therapy is prescribed under the supervision of a rehabilitation specialist.Long-term cyclic administration of substitutes of natural cartilage components - chondroprotective drugs - is also carried out.
Careful: In the third degree, arthrosis of the knee joint cannot be cured with the help of chondroprotectors..
Surgical treatment
Effective treatment of late arthrosis is only surgical - replacement of a joint that has lost its function with an endoprosthesis.
However, we must remember:
- in old age, the healing of the prosthesis is slower
- After the operation, there may be pain for a year
- long-term rehabilitation with mechanotherapy and comprehensive exercise therapy is needed
If the patient refuses the operation, then conservative supportive treatment is prescribed, the purpose of which is to fight pain and preserve the motor function of the knee.
What is arthrosis of the knee joint often confused with - gonarthrosis?
- During the diagnosis of gonarthrosismistakes occur as often, if not more often, than in the diagnosis of hip diseases.
- Below is a list of diseases that are most often confused with arthrosis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis).
- From the practice of Dr.Evdokimenko,Most often, arthrosis of the knee joint is confused with the following diseases:
Damage to the meniscus (meniscopathy) and blockage of the knee joint
Meniscus injuries and knee impingements occur in people of all ages, young and old.Men and women get sick equally often.Usually a knee joint is damaged.
Unlike gonarthrosis, the disease develops quickly.As a rule, after an unsuccessful movement while walking, running or jumping, a person hears a crack in the knee and feels acute pain in the joint.After 10-15 minutes, the acute pain subsides a little and the person can move.But the next day or the next day, the knee swells and the pain intensifies again.
Without proper treatment, the disease continues for years - the pain either subsides or appears again.But compared to gonarthrosis, meniscopathy rarely causes deformation of the bones of the knee joint - unless damage to the meniscus causes the development of knee arthrosis.And this, it should be noted, also happens quite often.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint (coxarthrosis)
The diagnosis of "gonarthrosis" is often mistakenly made with "referred" pain, which often occurs with arthrosis of the hip joint and extends from the hip joint to the knee.
But these conditions are very easy to distinguish - with arthrosis of the hip joint, the mobility of the knee does not decrease at all, the knee bends and straightens easily and without pain.
But the ability of a person suffering from arthrosis of the hip joint to rotate the leg "from the hip" and spread the legs to the sides is significantly reduced.
A person suffering from gonarthrosis, on the contrary, easily rotates the leg from the hip and easily spreads the legs to the sides.But he bends his knee with difficulty and sits down in pain.
Arthritis
The knee joints are the most vulnerable joints of the human body.In addition to arthrosis and meniscopathy, knee joints can be affected by any of the arthritis described in the second part of the book - reactive, rheumatoid, psoriatic, gout, ankylosing spondylitis and articular rheumatism.
Arthritis affects people of any age, but most often the onset of the disease occurs in young people.
With arthritis, one or both knees can become inflamed.
A characteristic feature of arthritic inflammation of the knee joint is a rapid onset (within 1-3 days), with visible swelling and swelling of the knee, as well as increased pain in the affected joint at night (around 3-4 in the morning).This means, the pain at night, when resting, can be stronger than when walking.With arthrosis, as you remember, the pain decreases at night.
Moreover, almost every arthritis leads to inflammation of not one, but several joints at the same time: in addition to the knees, the joints of the fingers and feet, elbow joints, ankle joints and heel tendons become inflamed and swollen in any combination.
Vascular pain in the knees
These pains, which arise due to poor blood circulation in the knee joints, are familiar to many people.They usually begin during adolescence, a period of active growth—as vascular development in fast-growing adolescents often does not keep pace with accelerated bone growth.
Once it happens, vascular pain in the knees can accompany a person almost throughout his life.But their intensity usually decreases after 18-20 years (and does not increase with age, as happens with arthrosis).And unlike the pain of arthrosis, vascular pain in the knees is not associated with reduced mobility of the knee joints.
Pain sensations are usually symmetrical, that is, they are equally pronounced in the right and left knees;occur when the weather changes, in the cold, during cooling and after physical activity.At such times, sufferers complain that their knees are "twisted".
In most cases, vascular pain in the knees is easily eliminated by rubbing warm ointments, massage and self-massage (vigorous rubbing of the knees) or by taking vasodilator drugs.No specific therapy is required for this condition.
Inflammation of the knee tendons (periarthritis of the bursa anserina)
Women are mostly affected, more often over the age of 40.The pain usually occurs when walking down stairs or when carrying heavy objects or heavy bags.When walking calmly on a flat surface, pain is extremely rare.
The pain caused by periarthritis does not extend to the entire knee.It focuses exclusively on the inside of the knees, about 3- below the point where your knees would touch when you bring your feet together.And unlike arthrosis, with periarthritis there is no limitation of knee mobility;the leg flexes and extends at the knee as expected, fully.
































